With many around the world closely following the fiercely contested rematch between U.S. President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump, a new Pew Research Center survey finds that, internationally, Biden is viewed more positively than his rival.
Across the 34 nations polled, a median of 43% have confidence in Biden to do the right thing regarding world affairs, while just 28% have confidence in Trump. The gap between ratings is quite wide in many countries, especially in Europe. Biden’s confidence rating is at least 40 percentage points higher than Trump’s in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland and Sweden.
However, there are exceptions. There is no statistically significant difference in ratings of Biden and Trump in eight nations we surveyed. And people in Hungary and Tunisia give Trump more positive reviews than Biden, although neither leader gets especially high marks there. (The survey was conducted before Trump’s conviction in a state criminal trial in New York.)
Even though Biden gets better assessments than Trump globally, ratings for the current U.S. president are down since last year in 14 of 21 countries where trends are available, including by double digits in Australia, Israel, Japan, Poland, South Africa, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
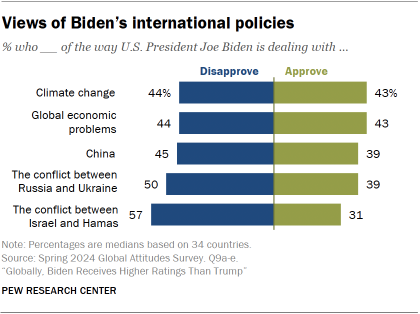
The survey included a series of questions about how Biden is handling major international issues. Overall, opinions are divided on how he is dealing with climate change and global economic problems.
Across the 34 countries polled, a median of around four-in-ten approve of how Biden is dealing with China and with the war between Russia and Ukraine (39% each).
The president gets his most negative reviews on his handling of the Israel-Hamas war: A median of just 31% approve of the way he is handling the conflict, while 57% disapprove.
Six-in-ten Israelis disapprove of how Biden is handling the war, including 53% of Jewish Israelis and 86% of Arab Israelis.
Of the predominantly Muslim nations surveyed, large majorities in Malaysia, Tunisia and Turkey also disapprove of Biden’s handling of the Israel-Hamas war. Opinion is divided on this issue in Bangladesh.
The new survey finds that overall attitudes toward the United States are generally positive: A median of 54% across the nations polled have a favorable view of the U.S., while 31% have a negative opinion.
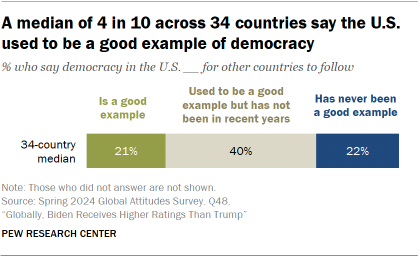
However, criticisms of American democracy are common in many nations. We asked respondents whether U.S. democracy is a good example for other countries to follow, used to be a good example but has not been in recent years, or has never been a good example.
The predominant view in most countries is that the U.S. used to be a good model but has not been recently. Overall, a median of 21% believe it is currently a good example, while 22% say it has never been a good model for other countries.
In eight of the 13 countries where trends are available, fewer people say American democracy is a good example than said so in spring 2021, when we last asked this question.
For this report, we surveyed 40,566 people in 34 countries – not including the U.S. – from Jan. 5 to May 21, 2024. In addition to this overview, the report includes chapters on:
Views of the U.S.
At least half of those in most countries surveyed express a favorable opinion of the U.S. Poles are the most positive, at 86% favorable. Of the European nations surveyed, ratings also lean positive in Italy, Hungary and the UK. Elsewhere in Europe, however, opinions tend to be closely divided.
Attitudes toward the U.S. are largely favorable in the Asia-Pacific nations polled, especially Japan, the Philippines, South Korea and Thailand. However, most Australians and Malaysians give the U.S. poor marks.
In the Middle East-North Africa region, a 77% majority of Israelis view the U.S. favorably, although this is down from 87% last year. Large majorities in Tunisia and Turkey offer an unfavorable opinion.
The U.S. gets mostly positive ratings in the sub-Saharan African and Latin American nations surveyed. Two-thirds or more see the U.S. favorably in Colombia, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria and Peru.
Confidence in Biden, Trump and other world leaders
Pew Research Center has explored attitudes toward American presidents for over two decades, finding significant shifts in opinions over the years. Data from four Western European nations that we have surveyed consistently – France, Germany, Spain and the UK – shows long-term trends in views of recent presidents.
George W. Bush received low and declining ratings during his time in the White House, while Barack Obama got mostly high marks. Attitudes toward Donald Trump were overwhelmingly negative throughout his presidency. Biden has consistently received more positive reviews than his predecessor, but his ratings have declined in these four countries during his time in office.
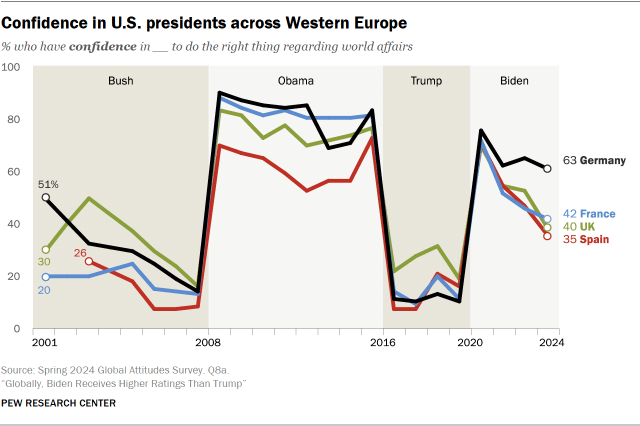
There are nine nations in this year’s survey where six-in-ten adults or more express confidence in Biden. Four are in Europe (Germany, the Netherlands, Poland and Sweden), two are in the Asia-Pacific region (the Philippines and Thailand) and three are in sub-Saharan Africa (Ghana, Kenya and Nigeria).
Since last year, confidence in Biden has dropped significantly in 14 nations: Seven in Europe, plus Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, Mexico, South Africa and South Korea. Biden gets his lowest ratings in Turkey and Tunisia, where only about one-in-ten express confidence in him.
The two countries where at least six-in-ten adults have confidence in Trump are Nigeria and the Philippines. Like Biden, Trump gets one of his lowest ratings in Turkey, where just 10% view him favorably.
Confidence in Trump has increased slightly in a few European countries since we last asked about him in 2020, although his ratings remain quite low in Europe.
In contrast, Trump’s ratings have become more negative in Poland since 2019, which was the last year we asked about him there. Israeli views toward the former president have also become more negative over the past five years.
In addition to exploring confidence in Biden and Trump, the survey asked about trust in French President Emmanuel Macron, Russian President Vladimir Putin and Chinese President Xi Jinping.
Overall, Macron receives the most positive ratings across the countries in the study, followed closely by Biden. The French president gets higher ratings than his U.S. counterpart in many of the European nations surveyed. Both Xi and Putin receive mostly poor marks across the countries in the study.
Differences by ideology, age and gender
Ideology
- In 17 of the 28 countries where political ideology is measured, people on the right are more likely to have a positive opinion of the U.S. than those on the left. For example, 65% of people on the right in Spain view the U.S. favorably, compared with 26% of people on the left.
- In 18 countries, people on the right are more likely to express confidence in Trump than those on the left. The gap is especially large in Israel, where 75% of those on the right have confidence in him, compared with just 23% of Israelis on the left.
- There are also some sizable ideological differences on views about Biden’s handling of the Israel-Hamas war. In several countries – including about half of the European countries surveyed – people on the right are more likely than those on the left to approve of how Biden is handling the conflict.
Age
- In several countries – including Canada, all Latin American countries surveyed and several countries in the Asia-Pacific region – adults under 35 are more likely to have a positive opinion of the U.S. when compared with adults ages 50 and older. Australia, Israel and Sweden are the only countries where younger adults have a less favorable view of the U.S.
- In Canada, Australia and seven of the 10 European countries surveyed, young adults are less likely than older adults to approve of how Biden is dealing with the Israel-Hamas war.
Gender
- Men have more confidence in Trump than women do in many of the countries surveyed. The largest difference is in the UK, where men are about twice as likely as women to trust the former U.S. president. In many of the countries surveyed, women are less likely than men to answer this question at all.






























Discussion about this post